Gynecologic Cancers- A Great Health Concern For Indian Women
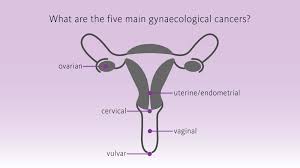

Gynecologic cancers continue to be a major health concern for Indian women, with cervical and ovarian cancers ranking among the most common. Despite increased awareness, India still sees over 1.2 lakh new cases of cervical cancer every year, resulting in more than 67,000 deaths. As these numbers remain alarmingly high, experts urge women to prioritise regular screenings, vaccination, and early consultation to improve outcomes and save lives.
Early Warning Signs Should Not Be Ignored: Timely Diagnosis Can Save Lives
The signs of these cancers can be missed if not taken seriously. Women should pay attention to unusual symptoms like very heavy or irregular periods, bleeding after menopause or sex, unusual vaginal discharge, a bloated stomach, loss of appetite, or a sudden increase in belly size due to fluid build-up. Sometimes, what looks like a harmless cyst or fibroid after an ultrasound test may be cancer. Blood tests can also give clues, and if anything seems suspicious, it’s important to consult a gynecologic cancer specialist without delay. Early treatment, especially surgery that eradicates the cancer in one go, gives the best chance of a cure.
Understanding the Causes: Age, HPV Infection, and Family History Play Key Roles
The causes of these cancers vary. The risk increases with age, and infections like HPV (human papillomavirus) are the main cause of cervical cancer. This virus is extremely common, and most women get exposed to it at some point. Some cancers, especially of the ovaries and breasts, can run in families and may be passed down through genes.
Nutrition and Lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle contribute to 20–60% of cancer cases worldwide. In gynecologic cancers, especially endometrial and ovarian, obesity and poor nutrition are major risk factors. Obesity alone is linked to nearly 40% of endometrial cancer cases. Low intake of fruits and vegetables and high consumption of processed foods increase cancer risk. On the other hand, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight control can reduce the risk of certain gynecologic cancers by up to 30%, making prevention largely lifestyle-driven.
Prevention is Possible: Vaccination, Screening, and Healthy Habits Can Reduce Risk
Prevention is possible in many cases. The HPV vaccine, which is recommended by the World Health Organisation and most health authorities, can prevent over 90% of cervical cancer cases. Regular tests like Pap smears and HPV screening can help catch problems early. Women with a strong family history of cancer can get genetic tests done and, if needed, take preventive steps like surgery. Healthy habits and regular checkups also go a long way in reducing cancer risk.
Modern Treatments Offer Hope: Advanced Surgeries, Targeted Therapies, and Innovative Approaches
Owing to medical advancements, treatment today is much more effective. Surgeons can now perform complex operations to remove cancer cells thoroughly. For certain cases, minimally invasive surgery using laparoscopy or robotics allows faster healing with smaller cuts. In some advanced cases, warm chemotherapy is given directly inside the abdomen to kill cancer cells more effectively. Alongside surgery, newer treatments like targeted drugs and immunotherapy are also being used based on each patient’s needs.
About the author- Dr. Upasana Palo
