Know It All About Vasculitis-Disease Of The Blood Vessels

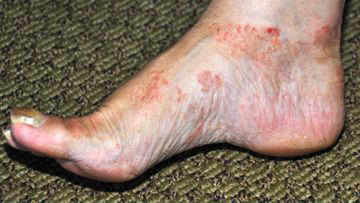
Vasculitis is an intricate health issue impacting the body’s blood vessels, resulting in inflammation, harm, and occasionally obstruction. Due to its diverse symptoms and potential complications, this condition poses challenges in both diagnosis and management. This article aims to delve into the complexities of vasculitis by examining its origins, signs, diagnostic procedures, available treatments, and prognosis.
What is Vasculitis?
Vasculitis, also referred to as angiitis or arteritis, denotes the inflammation of blood vessels. These vessels encompass a spectrum from tiny capillaries to major arteries, and the inflammation can impact various body regions, encompassing the skin, organs, and nervous system.
Causes of Vasculitis:
Vasculitis may be instigated by a variety of factors, including:
* Autoimmune Disorders: Often, vasculitis stems from an atypical immune system reaction wherein the body erroneously targets its blood vessels.
* Infections: Specific infections, like hepatitis B or C, and HIV, as well as bacterial or viral infections, have the potential to incite vasculitis.
* Allergic Reactions: Certain medications or allergens can precipitate an allergic response leading to vasculitis.
* Genetic Factors: Certain genetic inclinations might elevate the likelihood of vasculitis development.
Symptoms of Vasculitis:
The manifestations of vasculitis may fluctuate based on the size and site of the impacted blood vessels. Typical symptoms encompass:
* Tiredness
* Elevated body temperature
* Aches in muscles and joints
* Presence of skin eruptions or lesions
* Nerve-related issues like numbness, tingling, or weakness
* Dysfunction of organs such as kidneys or lungs
Diagnosis of Vasculitis:
Diagnosing vasculitis can be challenging and often requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests, including:
• Blood tests to check for signs of inflammation and specific antibodies.
• Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, or angiography, to visualize blood vessels.
• Biopsy of affected tissue to confirm inflammation in the blood vessels.
Treatment Options for Vasculitis:
Treatment for vasculitis aims to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and suppress the abnormal immune response. Depending on the severity and type of vasculitis, treatment may include:
• Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
• Immunosuppressive drugs to suppress the immune system.
• Biologic agents to target specific immune pathways.
• Plasmapheresis to remove harmful antibodies from the blood.
• Supportive therapies, such as pain management and physical therapy.
Outlook:
The outlook for individuals with vasculitis varies depending on the type, severity, and response to treatment. With early diagnosis and appropriate management, many people with vasculitis can achieve remission and lead active, fulfilling lives. However, some forms of vasculitis may be chronic and require long-term treatment and monitoring.
Conclusion:
Vasculitis is a complex condition that requires careful evaluation and management by healthcare professionals. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for vasculitis, individuals can take proactive steps to seek timely medical attention and improve their quality of life. Early detection and intervention are crucial in minimizing complications and maximizing outcomes for people living with vasculitis.
About the author- Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay, Academic Director, Asian Institute of Immunology & Rheumatology, Newtown, Kolkata.
